
Let’s start from some basics
Basic File sharing: Client-Server and P2P
Skip ahead if you know this part.
A few years ago the Internet was pretty easily divided into two groups: servers and clients. (Just like at a restaurant.) There weren’t that many servers, but their primary job was to hold web pages and files to be downloaded. They didn’t do much other than sit there and wait for people like you to request a web page or file. You, as the client, probably didn’t share any files or web pages with anyone. This segregation was primarily due to the fact that it takes a lot of outgoing bandwidth to share stuff. In a time before broadband DSL and cable modems, back in the days of dialup, most people didn’t have the bandwidth, let alone the knowhow to share stuff on their own. This old system was called client-server, appropriately enough, and it is still used today for the vast majority of stuff on the Internet, including web pages.
With the advent of broadband technologies such as DSL and cable modems, the everyday user like you suddenly has a big chunk of bandwidth, not only for download, but also upload. Sharing files directly from your computer (without first sending them to a server) is now a reality. This is where p2p comes in. The acronym p2p stands for peer-to-peer, which basically means client to client. That is, you download files from people like you instead of from big servers, and in turn they download files from you. You share your files, your friends share their files, and everyone talks directly to each other.
Introduction
Bit Torrent is a peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P) communication protocol. A Bit Torrent client is the application which uses that protocol. You can use Bit Torrent to share and download any type of file you want. It uses a principal called tit-for-tat. This means that in order to receive files, you have to give them. Bit Torrent downloads different pieces of the file you want simultaneously from multiple computers.
Unlike other download methods, Bit Torrent maximizes transfer speed by gathering pieces of the file you want and downloading these pieces simultaneously from people who already have them. This process makes popular and very large files, such as videos and television programs, download much faster than is possible with other protocols.
Developer
The protocol is the brainchild of programmer Bram Cohen, who designed it in April 2001 and released a first implementation on 2 July 2001. It is now maintained by Cohen’s company Bit Torrent, Inc.
How Bit Torrent works?
Before understanding how bit torrent works let us know some bit torrent jargon
- Seeder = A computer with a complete copy of a Bit Torrent file. Seeder’s uploads the file; to get a file you need at least 1 seed
- Leecher =People who download files but do not share files on their own computer with others (also known as a peer). Leecher’s downloads the file uploaded by a seeder (he can also upload the file for others to download)
- Tracker = A program that keeps track of who has what and what pieces or A server that manages the Bit Torrent file-transfer process
- Swarm = the group of computers involved with any one particular torrent. Or A group of computers simultaneously sending (uploading) or receiving (downloading) the same file. The number of computers that the swarm contains is found by adding the number of seeds to the number of peers.
- Ratio = the amount you have downloaded to the amount you have uploaded.
Users browse the web to find a torrent of interest, download it, and open it with a Bit Torrent client. The client connects to the tracker(s) specified in the torrent file, from which it receives a list of peers currently transferring pieces of the file(s) specified in the torrent. The client connects to those peers to obtain the various pieces. Such a group of peers connected to each other to share a torrent is called a swarm. If the swarm contains only the initial seeder, the client connects directly to it and begins to request pieces. As peers enter the swarm, they begin to trade pieces with one another, instead of downloading directly from the seeder.
Clients incorporate mechanisms to optimize their download and upload rates; for example they download pieces in a random order to increase the opportunity to exchange data, which is only possible if two peers have different pieces of the file.
Summary
- Bit Torrent client software communicates with a tracker to find other computers running Bit Torrent that have the complete file (seed computers) and those with a portion of the file (peers that are usually in the process of downloading the file).
- The tracker identifies the swarms, which is the connected computers that have all of or a portion of the file and are in the process of sending or receiving it.
- The tracker helps the client software trade pieces of the file you want with other computers in the swarm. Your computer receives multiple pieces of the file simultaneously.
- If you continue to run the Bit Torrent client software after your download is complete, others can receive .torrent files from your computer; your future download rates improve because you are ranked higher in the “tit-for-tat” system.
The big differences with Torrents compared to other P2P networks are:
a) I don’t have to give the whole file to each person to get it out there - I can give a bit to each person
b) Once I have given a bit out, its availability has just increased, because someone else can then also give it out, and so on and so on. the speed of a torrent will generally get better as more and more people want it - unlike Soul Seek or other P2P apps where you just wait longer to get it!!
c) Torrents technically aren’t illegal. After all, a torrent is just a tiny little file with no copyrighted content. It’s a bit muddy water here though, as they can facilitate the transfer of copyrighted content.
Indexing
The Bit Torrent protocol provides no way to index torrent files. As a result, a comparatively small number of websites have hosted the large majority of torrents linking to (possibly) copyrighted material, rendering those sites especially vulnerable to lawsuits. Several types of websites support the discovery and distribution of data on the Bit Torrent network.
Public tracker sites such as The Pirate Bay allow users to search in and download from their collection of .torrent files; they also run Bit Torrent trackers for those files. Users can typically also upload .torrent files for content they wish to distribute.
Private tracker sites such as Demonoid operate like public ones except that they restrict access to registered users and keep track of the amount of data each user uploads and downloads, in an attempt to reduce leeching.
There are specialized tracker sites such as FlixFlux for films, bitme for educational content, fullcaliber.be for metal music, PureTnA for pornographic content, and TV torrents for television series. Often these will also be private.
Search engines allow the discovery of .torrent files that are hosted and tracked on other sites; examples include Mininova, Monova, BTJunkie, Torrentz and isoHunt. These sites allow the user to ask for content meeting specific criteria (such as containing a given word or phrase) and retrieve a list of links to .torrent files matching those criteria. This list is often sorted with respect to relevance or number of seeders. Bram Cohen launched a Bit Torrent search engine on http://search.bittorrent.com/ that commingles licensed content with search results.
Limitations and security vulnerabilities
Lack of anonymity
Bit Torrent does not offer its users anonymity. It is possible to obtain the IP addresses of all current, and possibly previous, participants in a swarm from the tracker. This may expose users with insecure systems to attacks.
The leech problem
Bit Torrent file sharers, compared to users of client/server technology, often have little incentive to become seeders after they finish downloading. The result of this is that torrent swarms gradually die out, meaning a lower possibility of obtaining older torrents. Some Bit Torrent websites have attempted to address this by recording each user’s download and upload ratio for all or just the user to see, as well as the provision of access to newer torrent files to people with better ratios. Users who have low upload ratios may see slower download speeds until they upload more. This prevents (statistical) leeching, since after a while they become unable to download much faster than 1-10 kB/s on a high-speed connection. Some trackers exempt dial-up users from this policy, because they cannot upload faster than 1-3 kB/s.
The cheater problem
There are “cheating” clients like BitThief which claim to be able to download without uploading, and because of this can sometimes download faster than regular clients. Such exploitation negatively affects the cooperative nature of the Bit Torrent protocol.
- Keep seeding till you achieve at least a 1:1 RATIO!!!
- Once you have the file, it’s no good just closing your client and forgetting about it. In order to allow it to be shared for others you MUST continue to seed.
- You are not invisible when you are in a swarm. Others, including copyright owners if they so wished, can see your IP when you are downloading or uploading a file.
- If you use a torrent site which has a forum attached, take the time to say thanks to the poster of the torrent. It only takes a moment.
- The speed at which you download is determined by things such as the Seed to Peer ratio, the seed(ers) upload bandwidth and of course your available download bandwidth. Try to download torrents that have lots of seeders and few peers in order to get faster speeds.
1.Public tracker sites The Pirate Bay.org (my best site)
2.Private tracker sites Demonoid (for registered users)
3.FlixFlux for films
4.bitme for educational content
5.fullcaliber.be for metal music
6.PureTnA for pornographic content
7.ICTorrent.com a forum based torrent site also contains a large no of useful torrents.
Last words
Bit Torrent is perfectly legal to use. However, it is illegal to download copyrighted materials in most countries. So if the file you’re downloading is copyrighted, then what you’re doing is not legal. Also never upload any copyrighted material on net and never seed any such file. If you have read the above article carefully then you will notice that your IP Addresses are not hidden. Help to protect n prevent PIRACY.
References
1. HowStuffWorks.com
2. Wikipedia
3. Basic File sharing: Client-Server and P2P: Don’t remember the source it is somewhat like tweaking Bit torrent and so on…
4. Some Important Things to Remember: Taken from ICTorrent.com Forums but don’t remember the author.












 Wouldn't it be great if you recieve all your gmail account emails on your Outlook account, so that you can read and reply them without loging into Gmail.
Wouldn't it be great if you recieve all your gmail account emails on your Outlook account, so that you can read and reply them without loging into Gmail.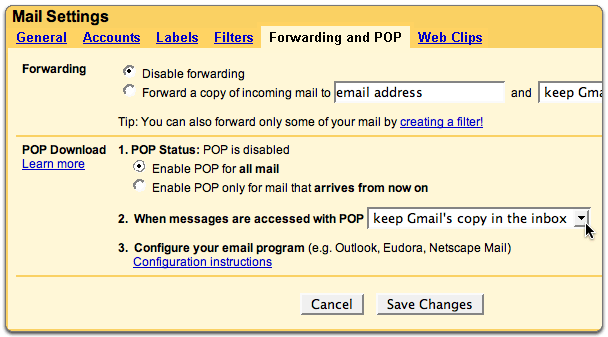
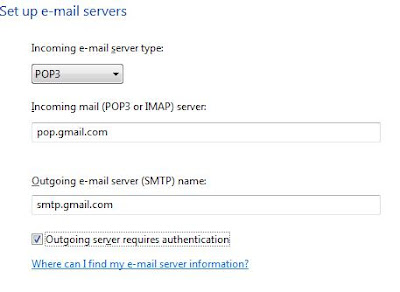 <
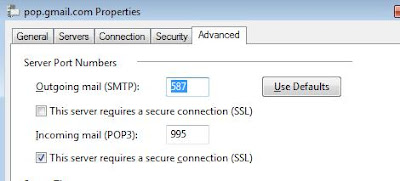
<

 You all have used
You all have used 



 Leaving your email as plain text in forums, on Twitter or on classified sites makes you an easy spam target: spam robots and email harvesters constantly browse these sites to collect new victim emails.
Leaving your email as plain text in forums, on Twitter or on classified sites makes you an easy spam target: spam robots and email harvesters constantly browse these sites to collect new victim emails.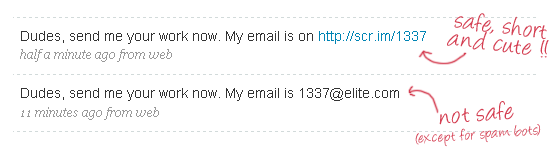
 Page Rank as the name says it is the ranking of a particular page based on different aspect that we have discussed below, but before that lets have a proper introduction of Page Rank.
Page Rank as the name says it is the ranking of a particular page based on different aspect that we have discussed below, but before that lets have a proper introduction of Page Rank.